Scroll down for the History of the “Royal Enfield Marque” and “Royal Enfield – Since 1901”

History of the Royal Enfield Marque
Royal Enfield is the world’s longest surviving motorcycle marque. In addition, throughout much of its life, Enfield was a real pioneering company, often at the very forefront of new design and technology. But what of its origins you may ask ?
Well, these go back to the middle of the 19th century, when the firm of George Townsend and Co. was formed in the tiny village of Hunt End, near the Worcestershire town of Redditch. George Townsend’s operation specialised in sewing needles and machine parts. As with many similar engineering concerns, Townsends firm kept the business going by tackling many other projects, although they retained their special skills in needle manufacture. Thus it was during the 1880’s they became involved with the burgeoning pedal-cycle trade. Their work in this field was to provide much useful experience for the new era of internal combustion vehicles, which was just around the corner.
By 1890, George Townsend and Co. had become a Limited Company and was manufacturing its own brand of bicycle, together with many component parts and accessories for sale to the cycle trade. Several changes were to occur over the next couple of years, with Albert Eadie becoming Managing Director and Robert Walker Smith Works Manager, whilst the company was re-registered under the Eadie Manufacturing title. It was also during this same period that the brand name Enfield was first applied to its products – this being due to contracts with the Royal Small Arms factory in Enfield, Middlesex. This contract between Eadie Manufacturing and Royal Small Arms was to result not only in the creation of Enfield Manufacturing Co. Limited but also the word “Royal” subsequently being added to its name, this all taking place in 1893. It was this Royal Small Arms connection that was responsible for the famous trademark ‘Made Like a Gun’

By 1896, the New Enfield Cycle Co. had been formed to embrace both the bicycle manufacturing division of Eadie and the sales arm of Enfield. A further 12 months on and the ‘new ‘ section was dropped and the Enfield Cycle Co. was officially launched – a name it was to keep throughout its many years whilst located in the Redditch area
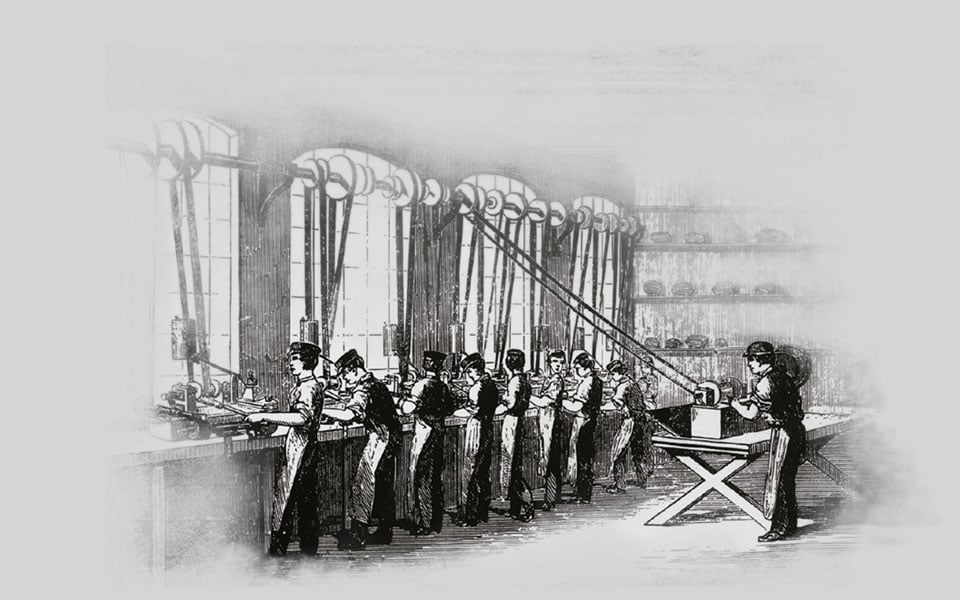
1891
R.W. Smith and Albert Eadie take over the Townsend Cycle Company in Redditch, UK. Soon after, they start supplying precision machine parts to the Royal Enfield Small Arms Factory in Enfield, Middlesex. Their undertaking is renamed the Enfield Manufacturing Company Limited.

1893
Enfield Manufacturing Ltd. becomes Royal Enfield – ‘Royal’ being taken from the Royal Small Arms Company. The trademark ‘Made like a gun’ is introduced.

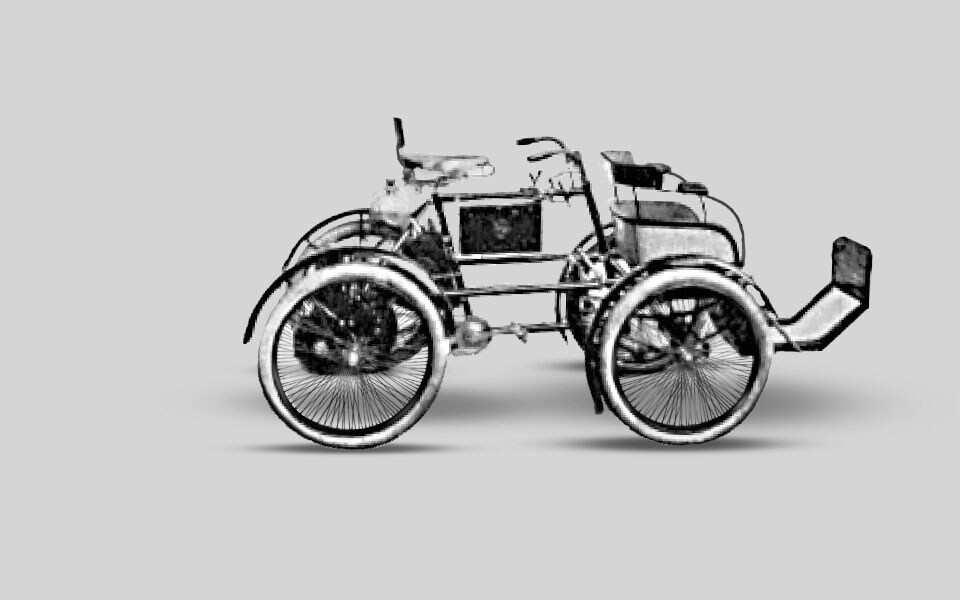
1898
R. W. Smith designs a prototype motorised vehicle, a four wheel bicycle known as a quadricycle. It uses a proprietary 1 1/2 hp De Dion engine.

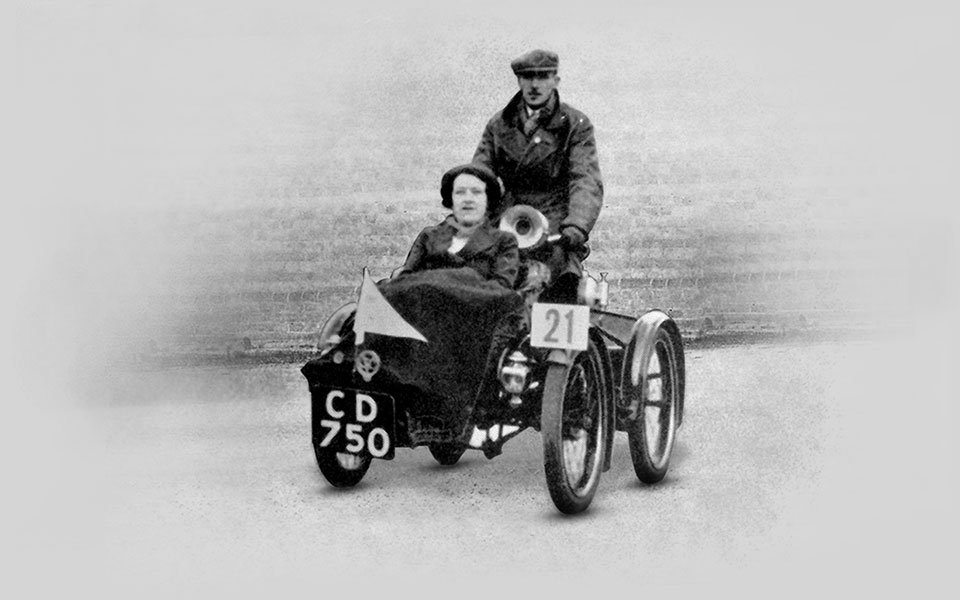
1900
Royal Enfield delves into motorsport when one of its quadricycles enters a 1000 Mile Trial. The event does much to persuade the British public about the viability of motorised transport.
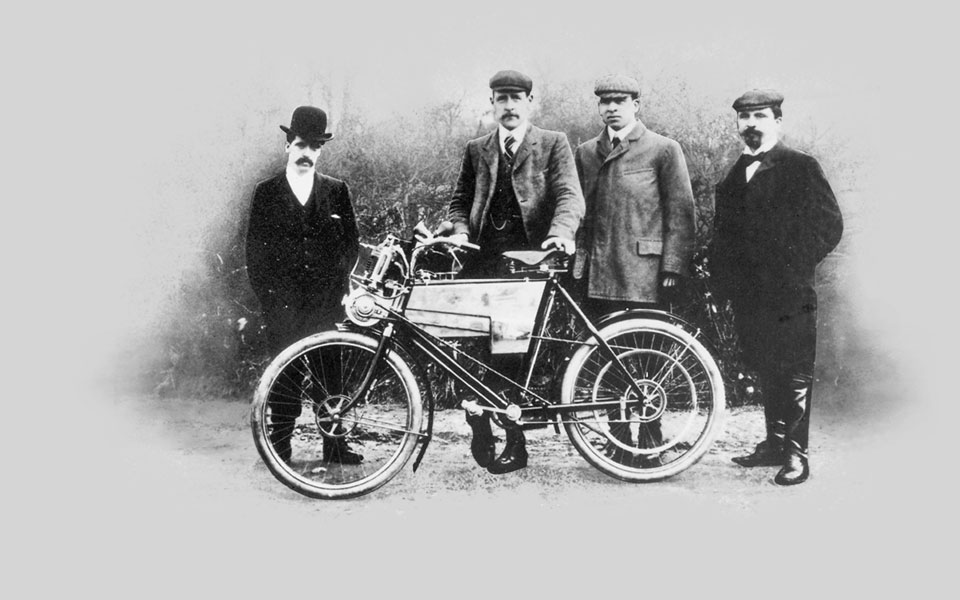
1901
The first Royal Enfield motorcycle is produced. Designed by R. W. Smith and Frenchman Jules Gotiet, it has a 1 1/2 hp Minerva engine mounted in front of the steering head. The final drive is at the rear wheel by means of a long rawhide belt.
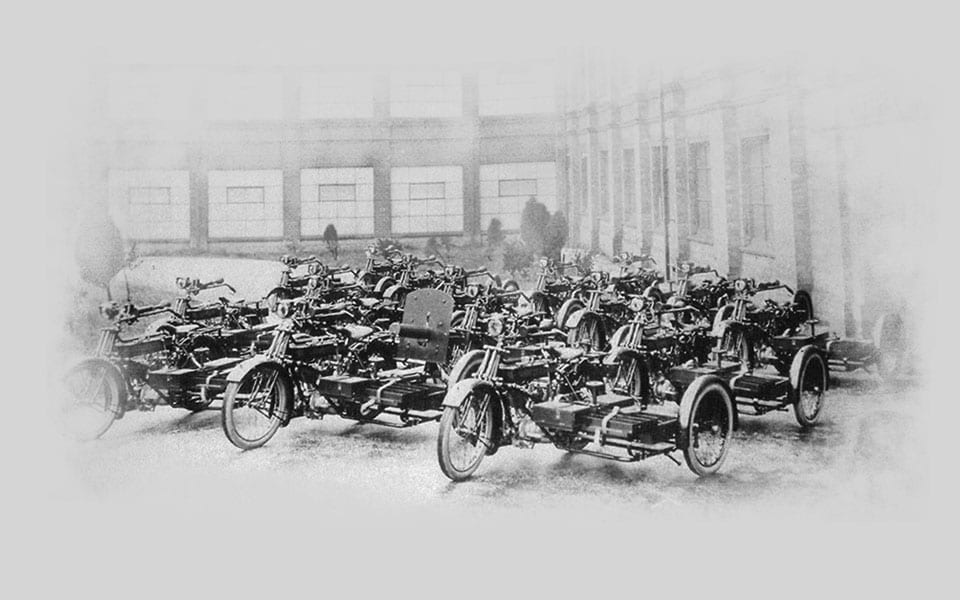
1914
Royal Enfield’s first 2-stroke motorcycle goes into full production. As Britain becomes more deeply involved in World War I, production ceases on all other Royal Enfield motorcycles barring this machine and the company’s biggest motorcycle, the 770cc 6 hp V-twin.
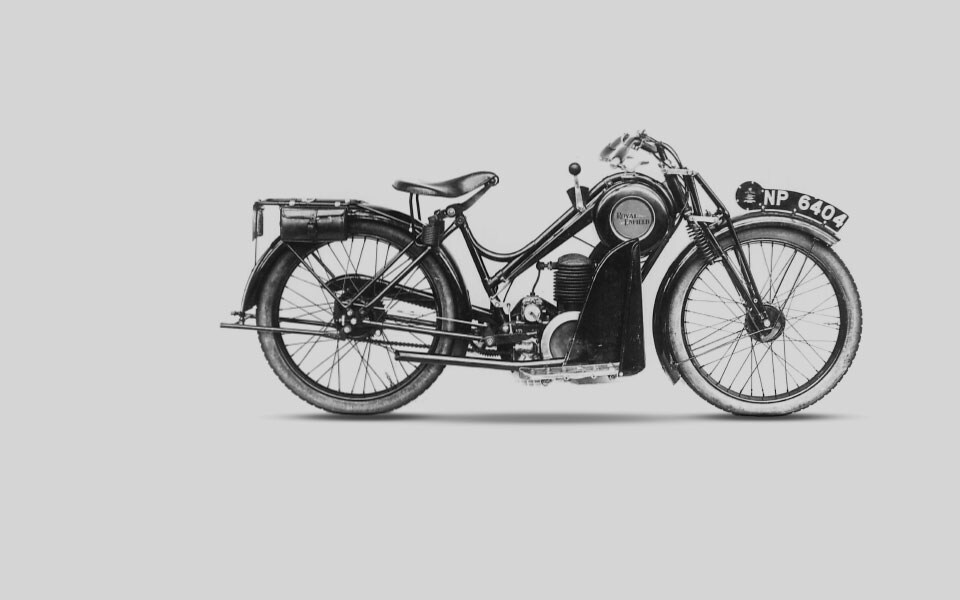
1924
Continuous development results in a range of 8 models, including the launch of the Sports Model 351, the first Royal Enfield 350cc OHV 4-stroke motorcycle with foot operated gear shift. It is powered by a JAP engine. A 225cc 2-stroke step-through ‘Ladies Model’ is also released.
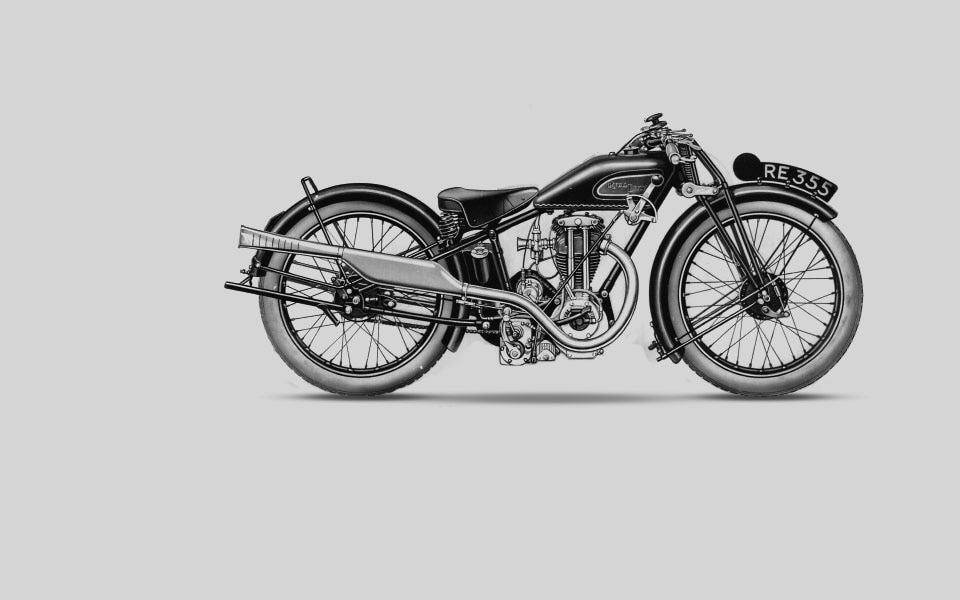
1928
Royal Enfield adopts saddle tanks in place of outmoded flat tanks. It is also one of the first manufacturers to change its front fork system from a Druid design to centre-sprung girder forks.
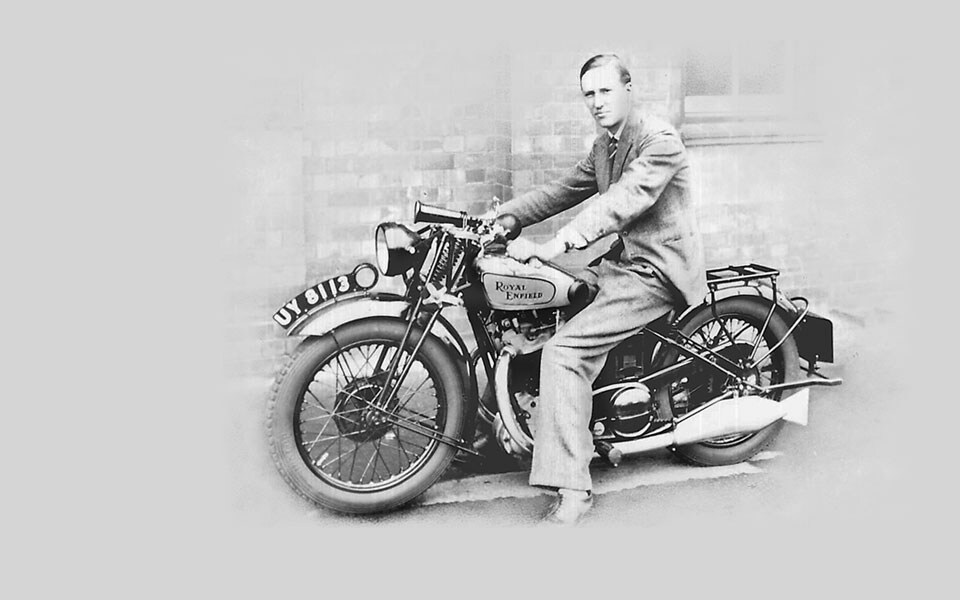

1930
The decade begins with a diverse eleven model range, from the 225cc 2-stroke Model A to the 976cc V-twin Model K. Also, the new 350 and 500cc side-valve and overhead valve machines with dry-sump lubrication are produced.
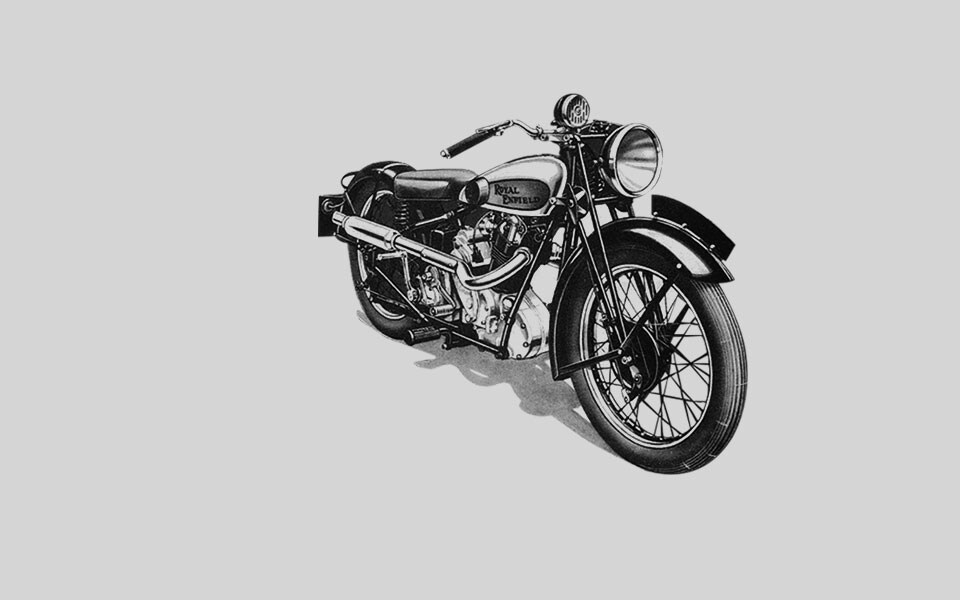

1932
The legendary “Bullet” motorcycle is born. It is first displayed in November 1932 at the important Earls Court Motorcycle Show in London. Three versions: 250, 350 and 500cc are available, all with inclined ‘sloper’ engines, twin-ported cylinder heads, foot operated gear shift and high compression pistons.
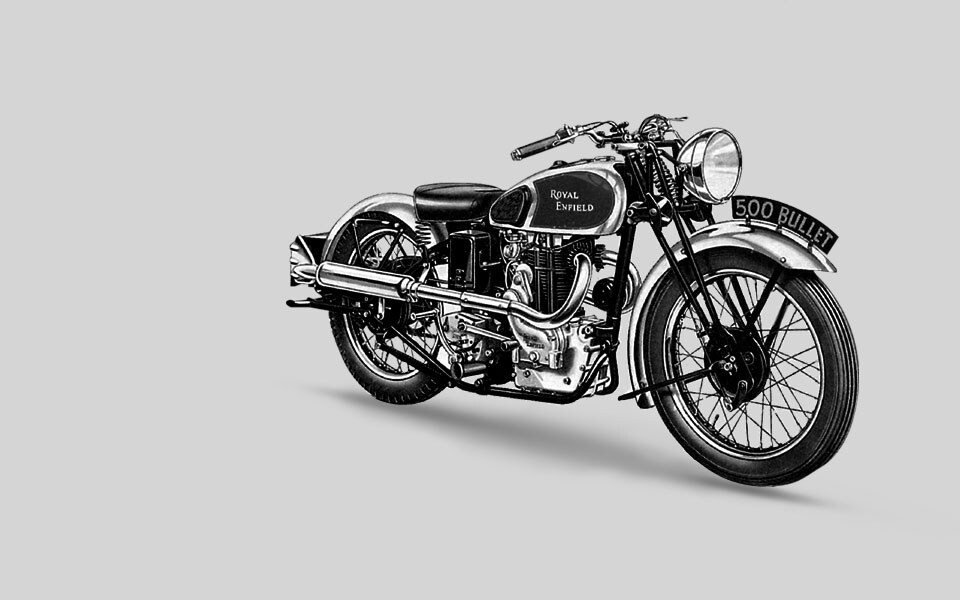

1936
The 500cc Bullet is radically changed the with the release of a new sporting version, the Model JF, featuring a 4-valve cylinder head.
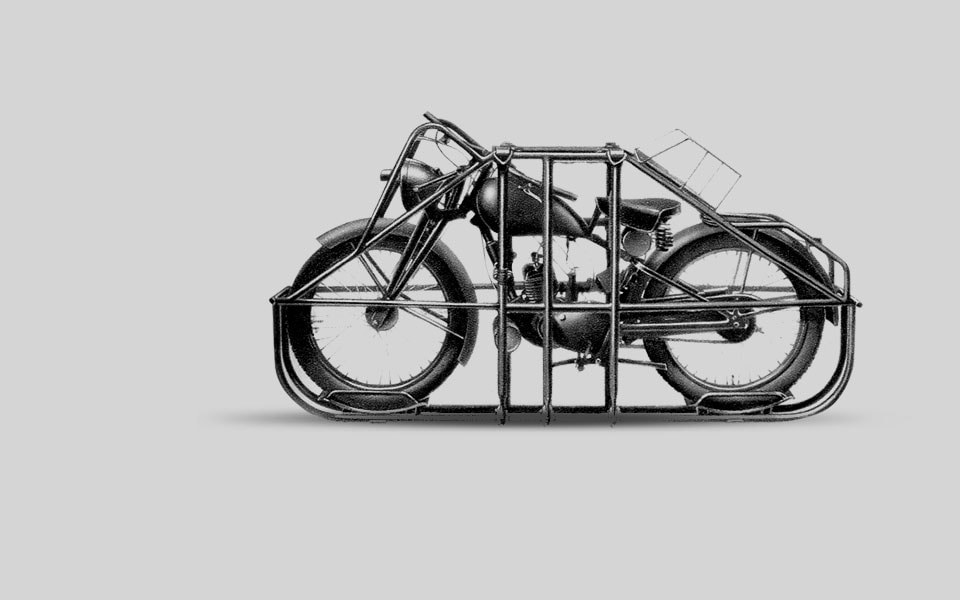
1939
Royal Enfield produces large quantities of motorcycles and bicycles during the Second World War. The most iconic military model is the 125cc ‘Airborne’ motorcycle known as the Flying Flea. This 125cc 2-stroke can be loaded into a specially fabricated parachute cradle and dropped with paratroops behind enemy lines.
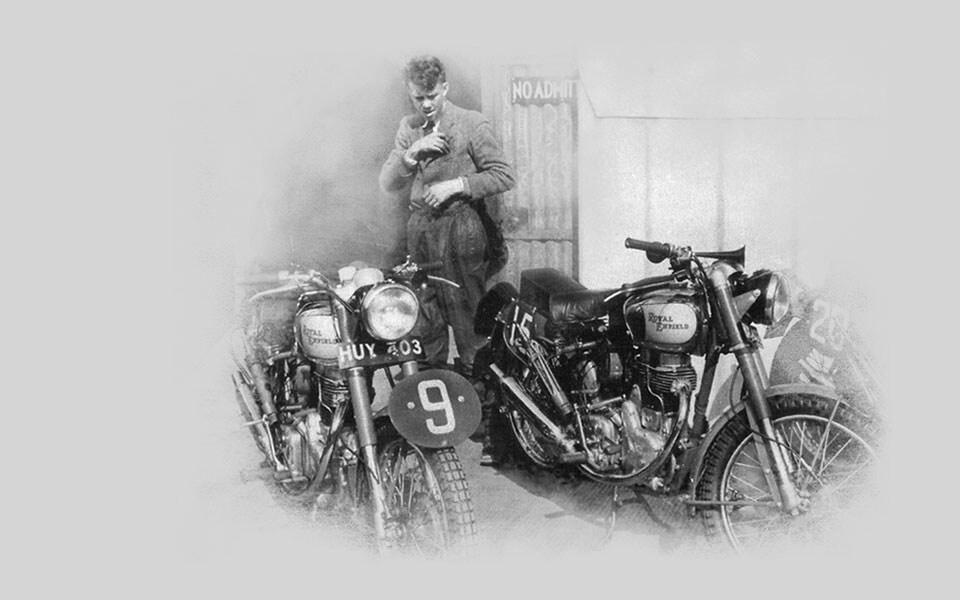

1948
The 350cc Bullet prototype, with radical swinging arm rear suspension is previewed in the Colmore Cup Trial of March 1948. Two Bullets form part of the victorious British team in the 1948 ISDT (International Six Day Trial), held in Italy. Both their riders win gold medals.
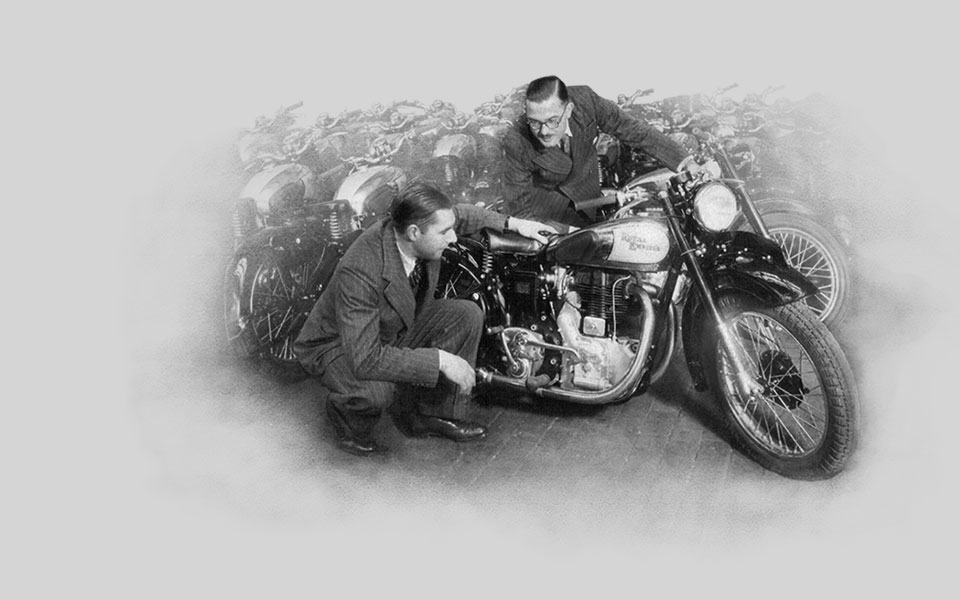

1949
The new 350cc Bullet and 500 Twin models are launched in the UK. Both bikes share the same frame, swinging arm suspension, telescopic front forks and gearbox. K. R. Sundaram Iyer launches Madras Motors to import British motorcycles into India. Besides Norton and Matchless machines, he sells Royal Enfields.
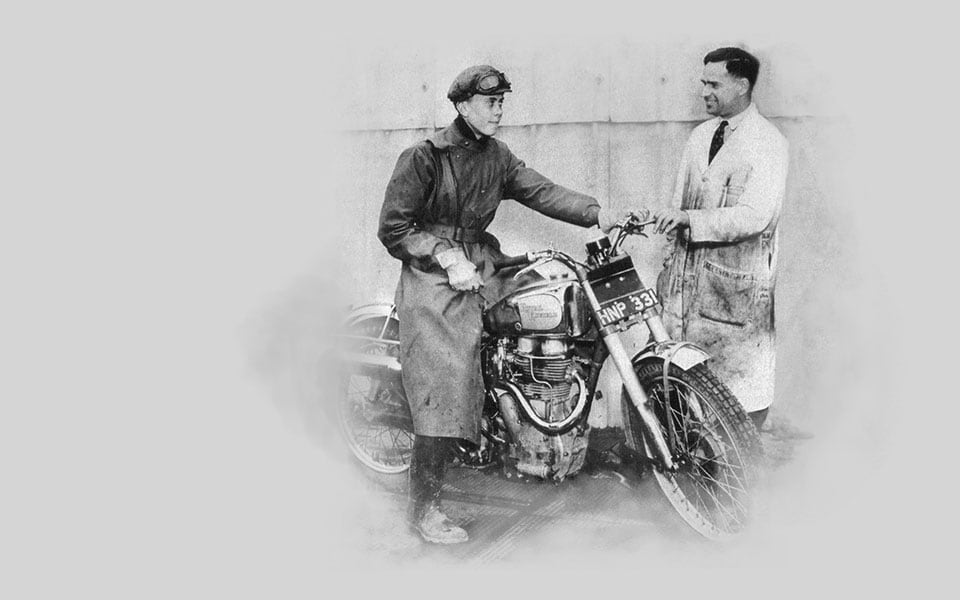

1952
Madras Motors receives an order from the Indian Army for 800 350cc Bullets. The motorcycles arrive from Redditch in early 1953 and prove to be a great success, being both hardy and easy to maintain. Johnny Brittain wins the prestigious Scottish Six Days Trial on his 350cc Bullet, “HNP 331”.
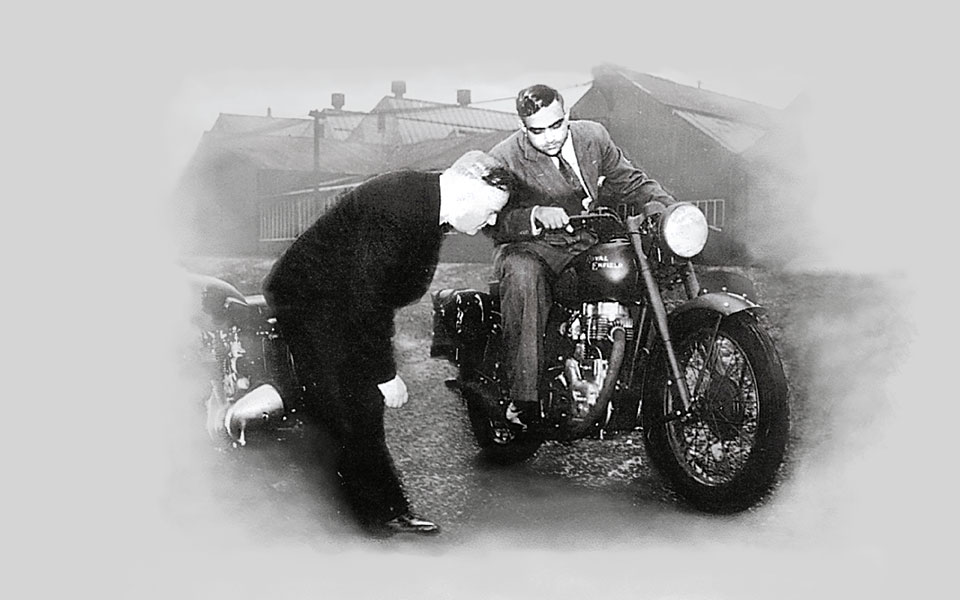

1955
The Redditch company partners Madras Motors in India to form ‘Enfield India’. Work commences on the construction of a purpose-built factory at Tiruvottiyur, near Madras.
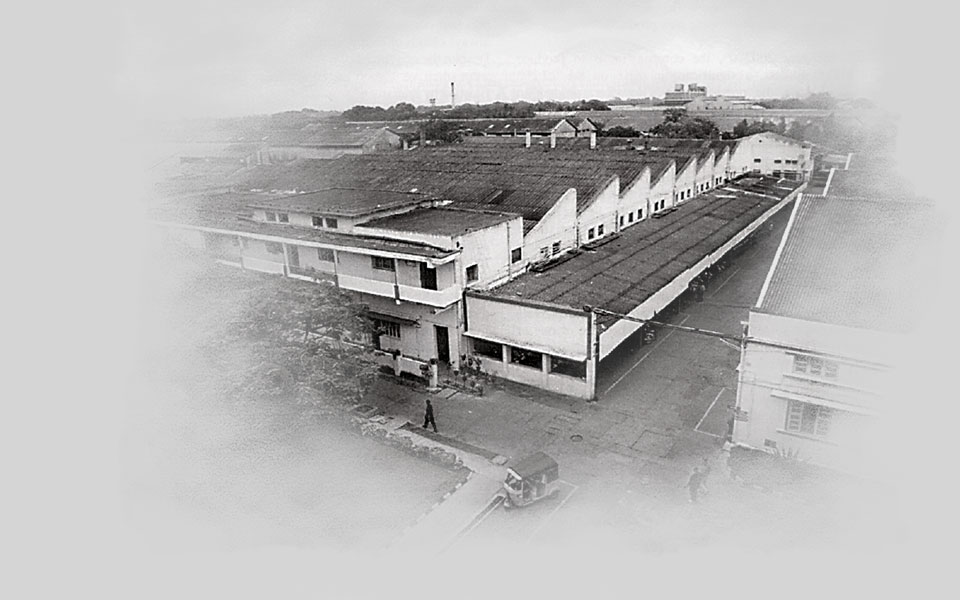

1956
The Tiruvottiyur factory opens and Bullets begin to be manufactured under license. Early production is based on machines that come from England in kit form which are then assembled in Madras. A total of 163 Bullets are built by the end of the year.
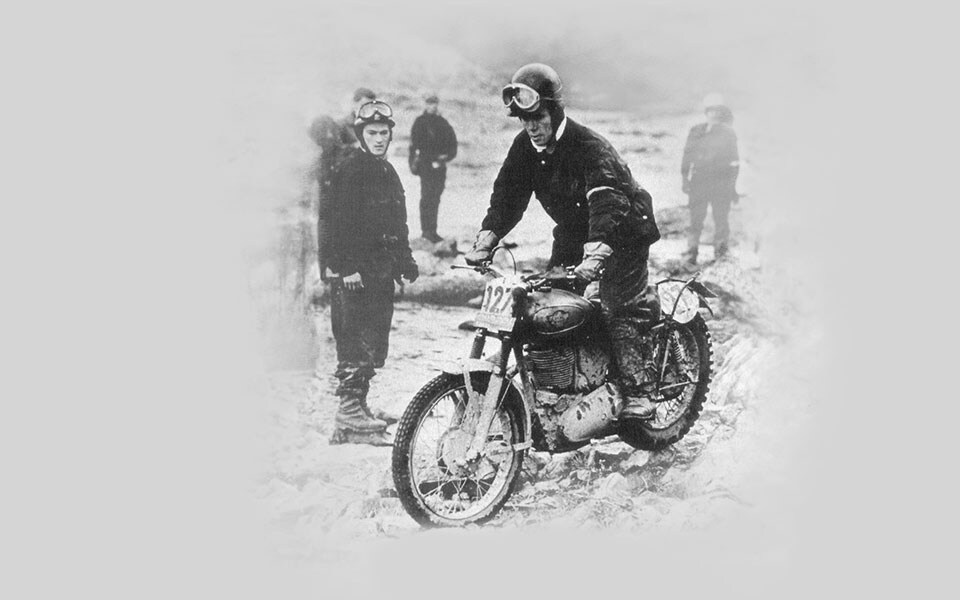

1957
Johnny Brittain wins the Scottish Six Days Trial on a Bullet for the second time and also finishes top of the British Trials Championship. The 250cc Crusader model is launched in Britain. Producing 13 bhp, the motorcycle features a unit construction engine and alternator electrics with coil ignition.
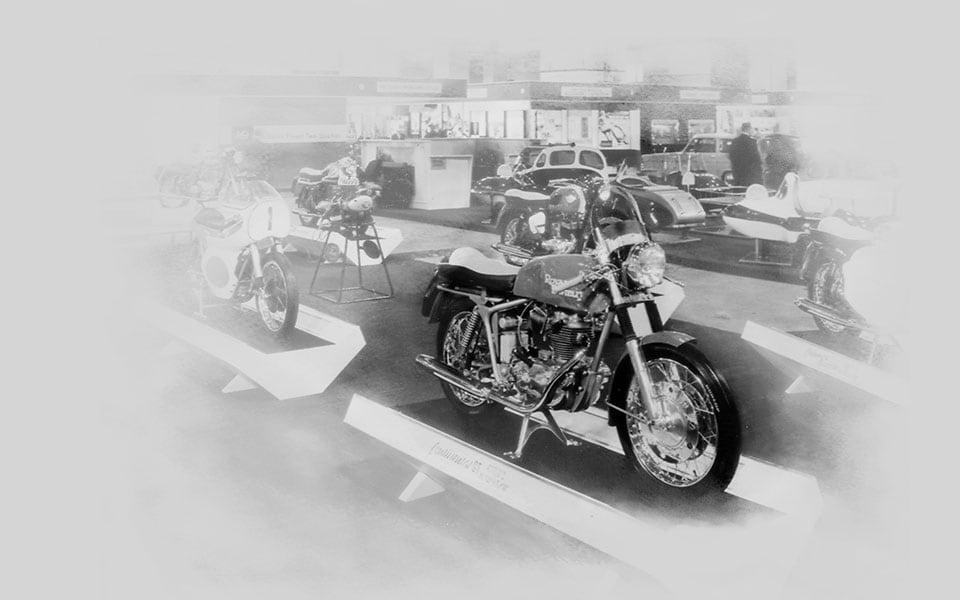

1964
The iconic Continental GT café racer is launched to great acclaim when a team of photojournalists ride it from John ‘o Groats to Lands End in under 24 hours, by way of 7 laps at the Silverstone circuit. The GT features a racing petrol tank, clip-on handlebars, rear sets, a humped race seat, rev counter and a swept-back exhaust.
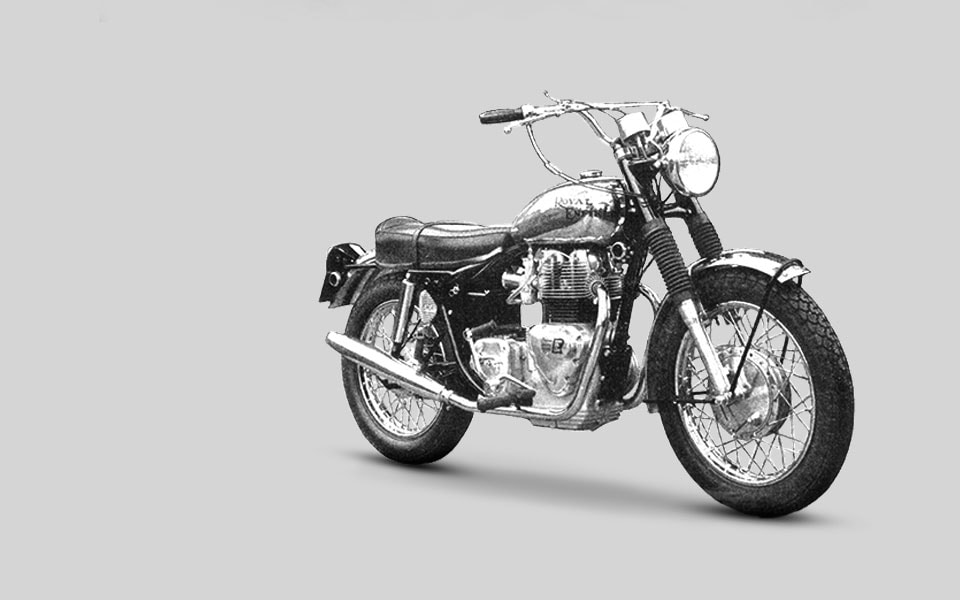

1967
With only two models left in production at the start of the year – the 250cc Continental GT and the 736cc Interceptor – Royal Enfield’s Redditch facility closes down. Production of the Interceptor continues at Enfield’s underground facility in Bradford on Avon.
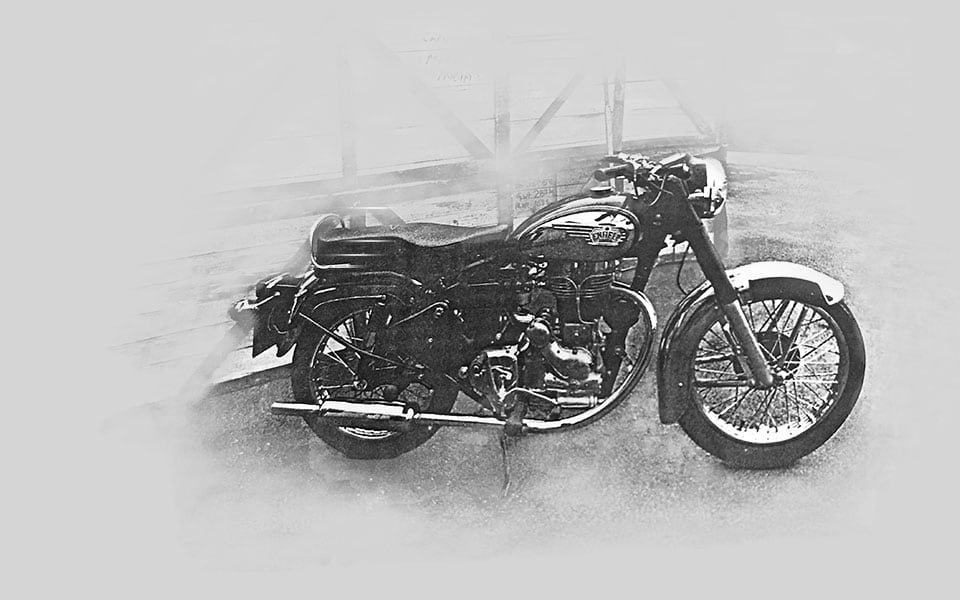
1977
Royal Enfield India begins exporting the 350cc Bullet to the UK and Europe. Sales grow rapidly as the bikes develop a following amongst classic British motorcycle enthusiasts.
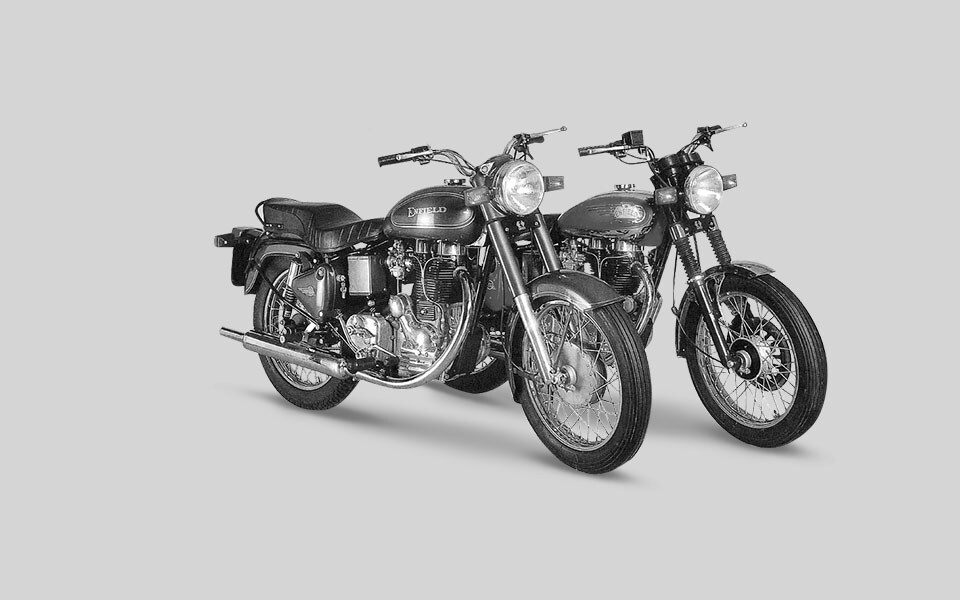

1989
A new 24 bhp 500cc Bullet is released. The bike is primarily aimed at export markets, where it is available in Classic, Deluxe and Superstar trim along with the 350.
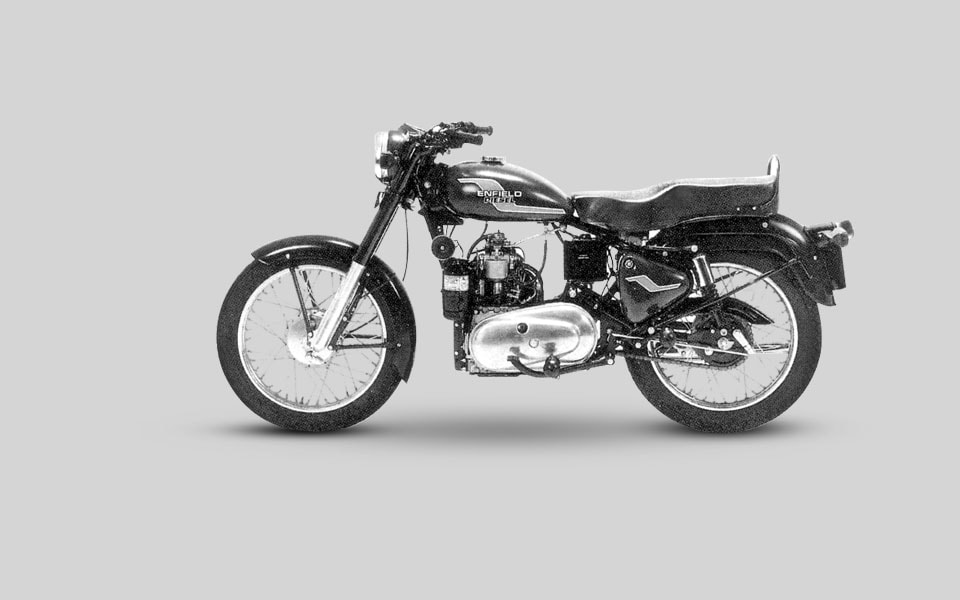

1993
Enfield India produces the world’s first and only mass-manufactured diesel motorcycle. Known as the Enfield Diesel, it used a highly fuel efficient 325cc power unit installed in the standard Bullet rolling chassis.
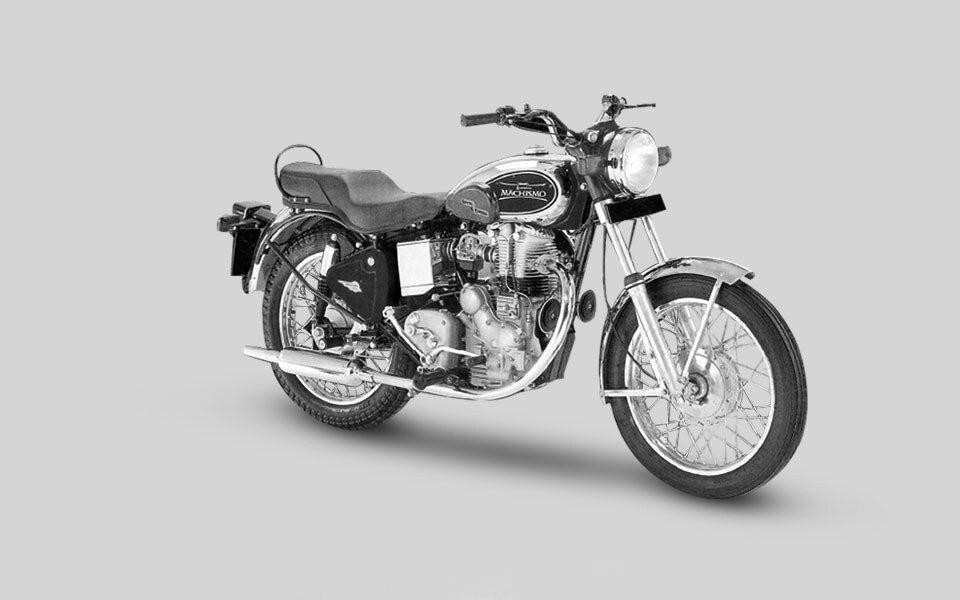

1994
The Eicher Group acquires Enfield India Limited. The company is renamed Royal Enfield Motors Limited.

1997
Forty Royal Enfield motorcycles tour Khardung La, the world’s highest motorable pass, setting a precedent for epic rides in some of the world’s most difficult terrain.
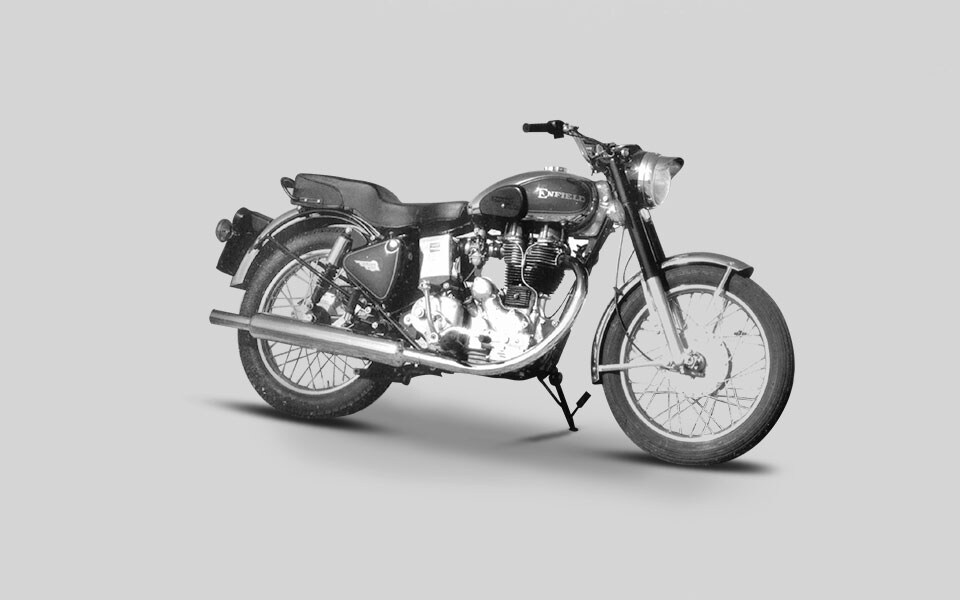

1999
Utilising the design skills of Austrian experts AVL, production of a revised 350cc all-aluminum lean-burn Bullet engine, known as the A350, begins at a new Royal Enfield plant near Jaipur, Rajasthan.
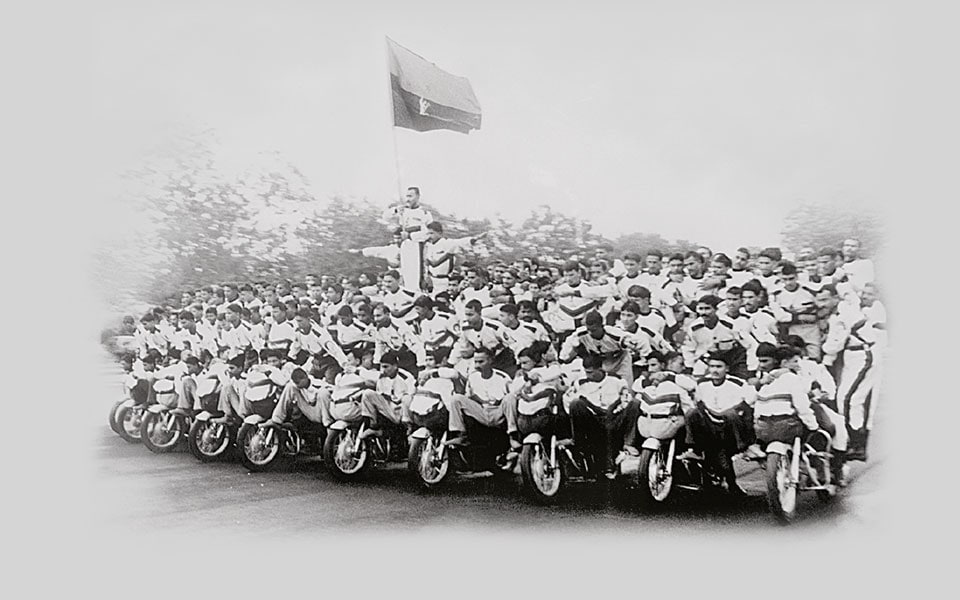

2001
The Daredevils, the motorcycle display team of the Indian Army Corps of Signals, Jabalpur, forms a human pyramid of 201 men on ten 350cc Enfield motorcycles, riding a distance of more than 200 metres.
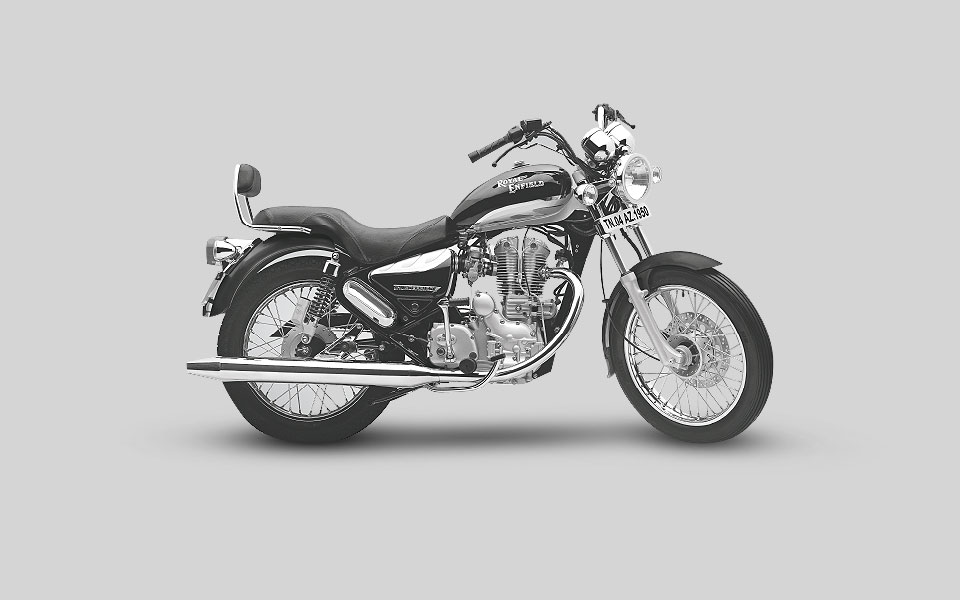

2002
The Thunderbird, a stylish lean burn cruiser is launched in India. It features the first 5-speed gearbox used on a Royal Enfield since 1965 in Redditch. More than a 1000 Royal Enfield motorcycles of all ages descend on Redditch for the Royal Enfield Owner’s Club Redditch Revisited event.
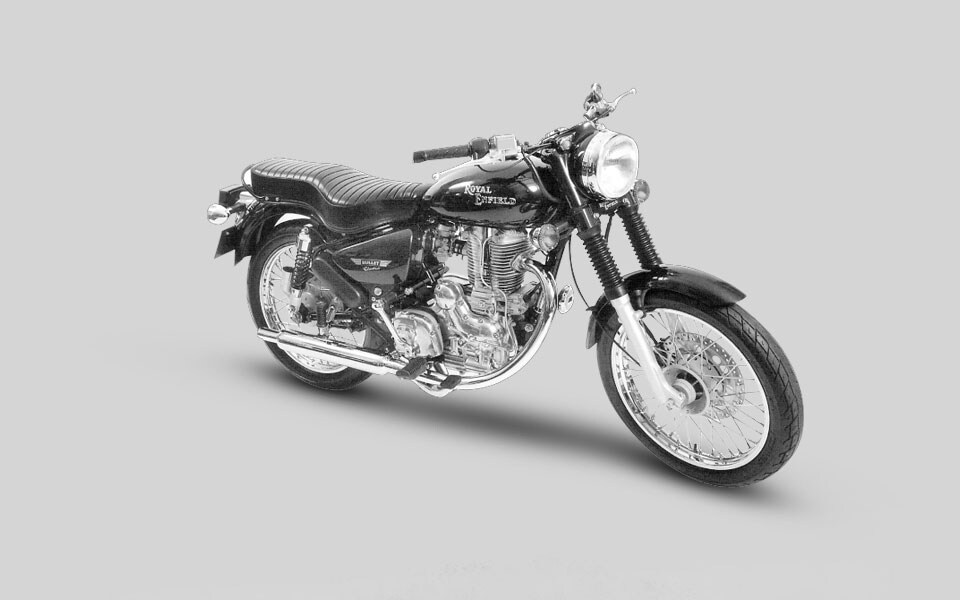

2004
The Electra X, an export Bullet with a 500cc version of the all-alloy lean burn engine, goes on sale. The retro-styled ‘Bullet Machismo’ is rated the ‘No.1 Cruiser’ in a TNS Autocar survey.

2005
Royal Enfield celebrates its 50th anniversary in India.
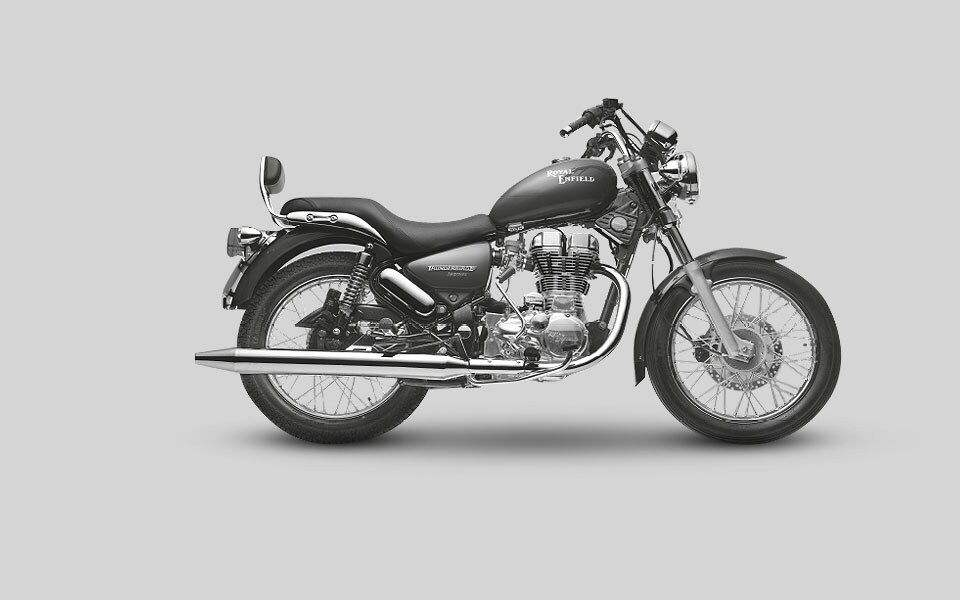

2008
Royal Enfield begins exporting the Classic, India’s first 500cc EFI, Euro III-compliant motorcycle, to European markets. The Thunderbird Twinspark is launched with the new Unit Construction Engine (UCE) in India.
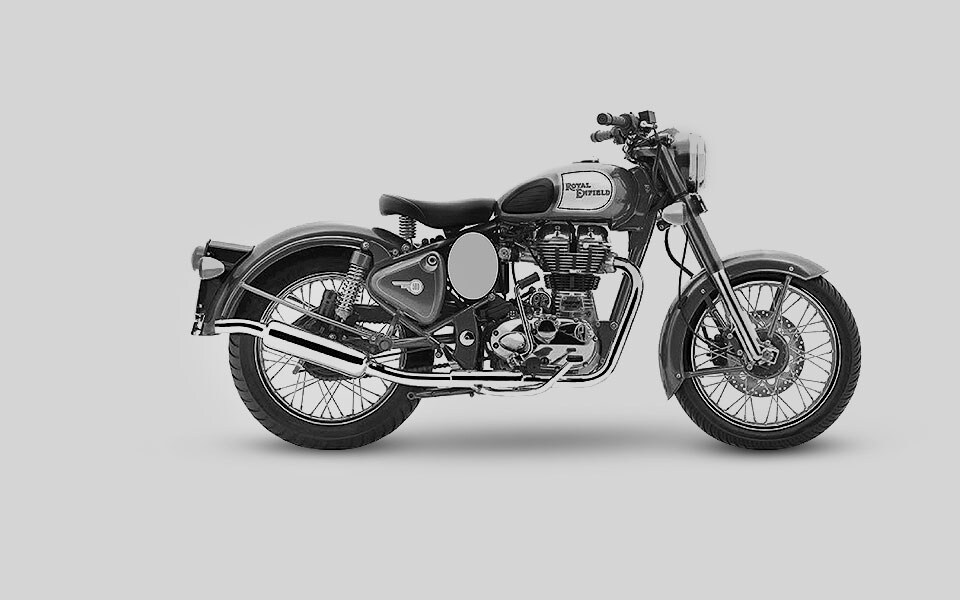

2009
The 500cc UCE engine is launched in India. The retro-styled Classic version achieves cult status immediately and sales grow rapidly.
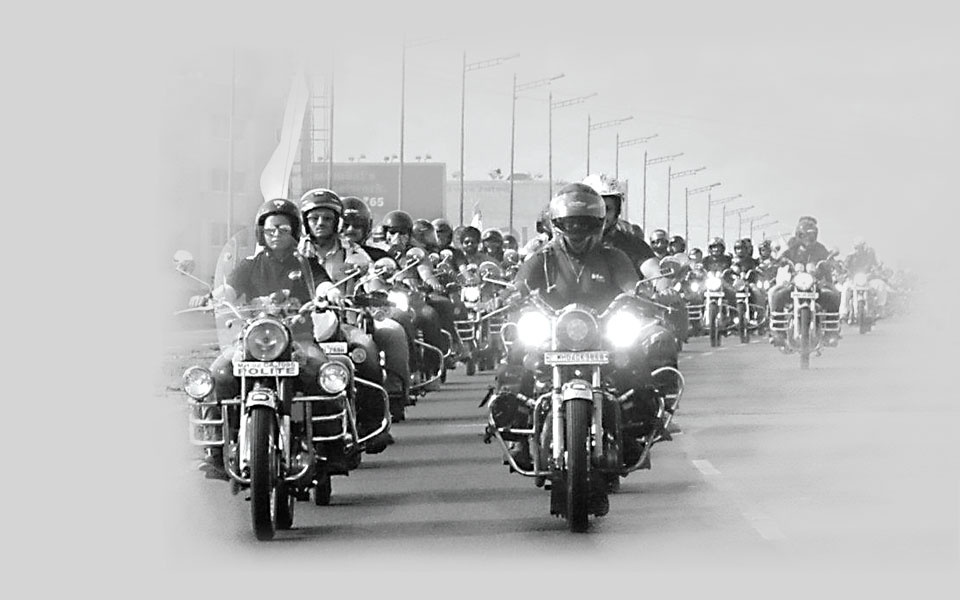

2011
The company launches its first annual ‘One Ride’, where all Royal Enfield riders across the world are encouraged to go for a ride on the first Sunday in April. Royal Enfield acquires 50 acres of land at Oragadam near Chennai for its new plant. A factory organised trip crosses the border with ‘Tour of Nepal’.
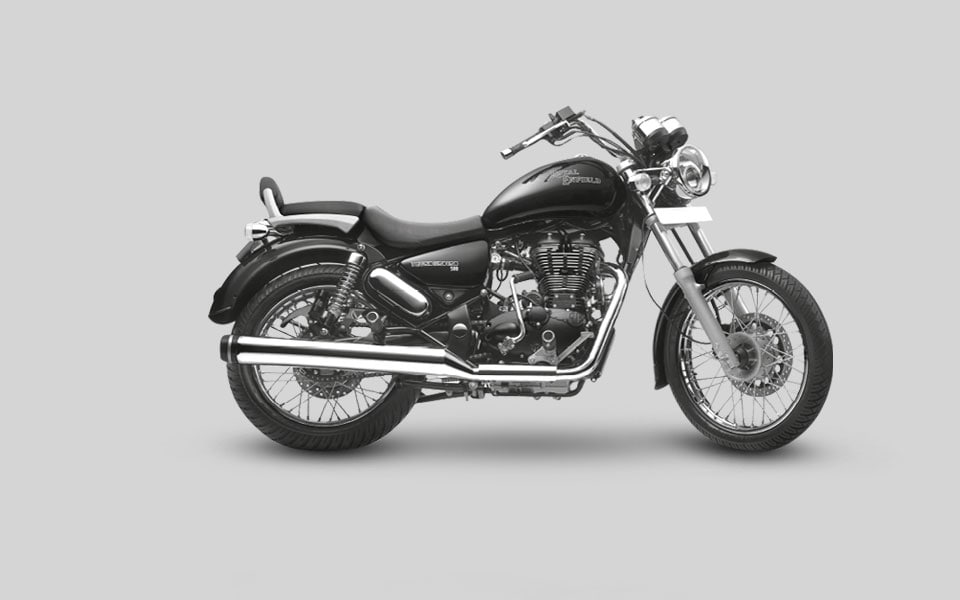

2012
Royal Enfield launches its first highway cruiser, the all-black Thunderbird 500. Work on the new Oragadam factory continues briskly while the Tiruvottiyur plant sets new production records.

2013
Royal Enfield commences manufacturing at its second facility at Oragadam, Tamil Nadu. With increased capacity, the state-of-art factory will be the nucleus of the company’s global ambitions in the future.
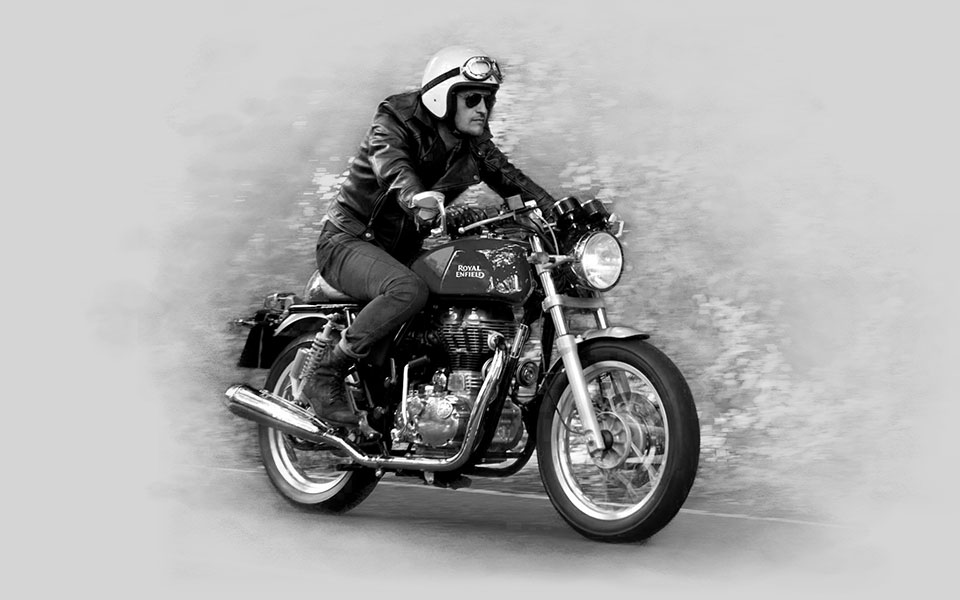

2013
Forty-eight years after developing the world’s first production café racer, Royal Enfield rolls out the all-new Continental GT. Rockers, critics and riders agree that it is the most fun one could ever have on a motorcycle.
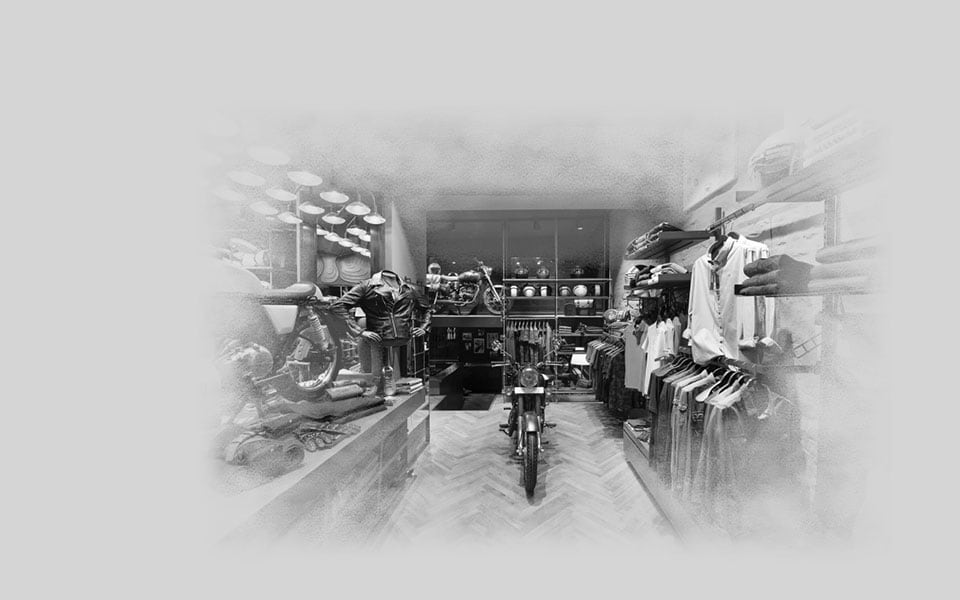

2014
Royal Enfield introduces a new retail experience with the opening of the first-of-its-kind exclusive gear store at Khan Market, New Delhi.

2015
Royal Enfield acquires erstwhile collaborators Harris Performance of the U.K., a motorcycle engineering and design firm to enhance its engineering and product design capabilities.

2015
Royal Enfield sets up its first direct distribution subsidiary outside India, in North America. Royal Enfield’s North American headquarters are located in Milwaukee, Wisconsin.
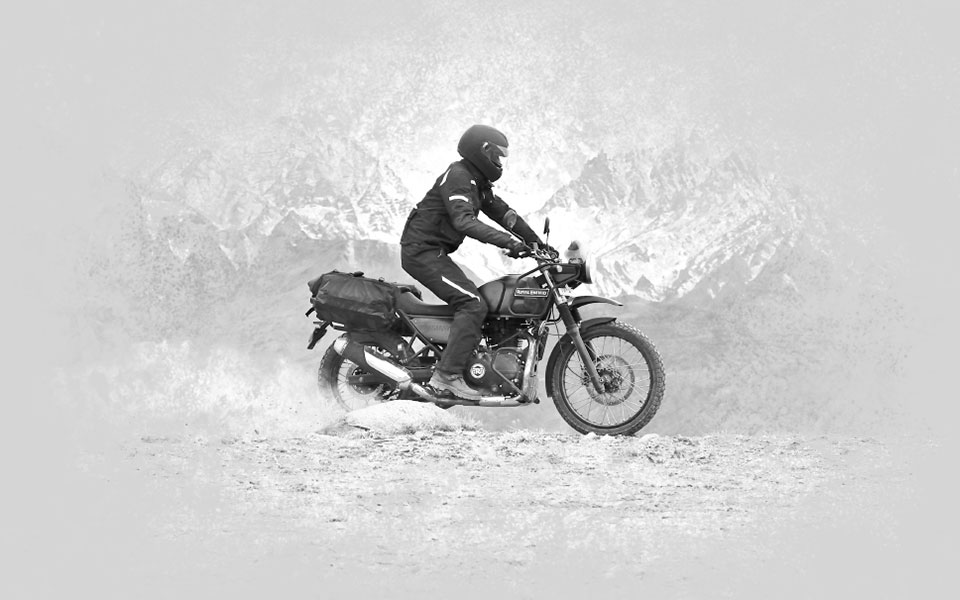

2016
Royal Enfield debuts the Himalayan. With the all-new LS410 engine and terrain-tested suspension, it promises the ride of a lifetime on all roads and no roads.
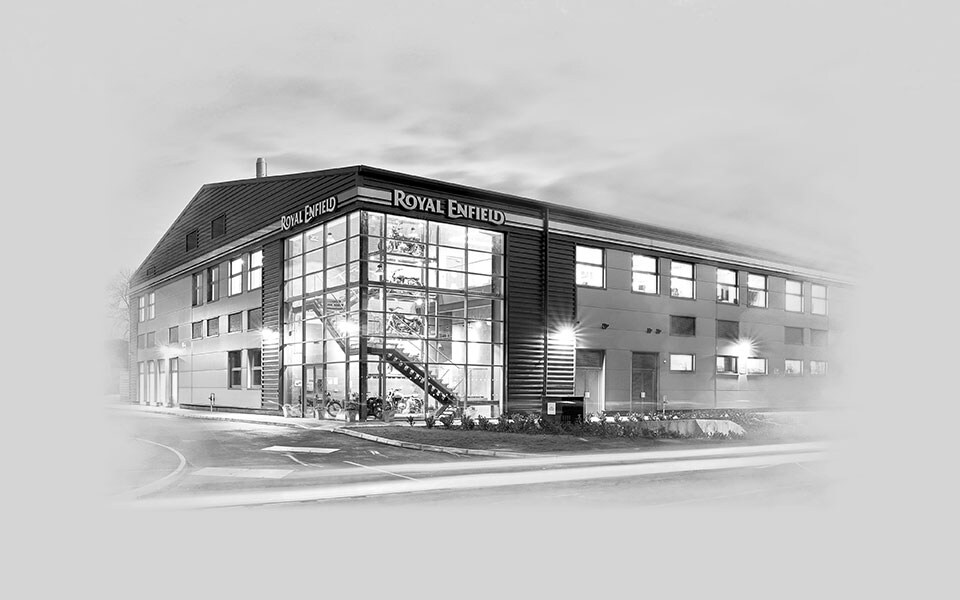

2017
Royal Enfield moves into its fully operational Technology Centre in UK at Bruntingthorpe Proving Ground, Leicester.
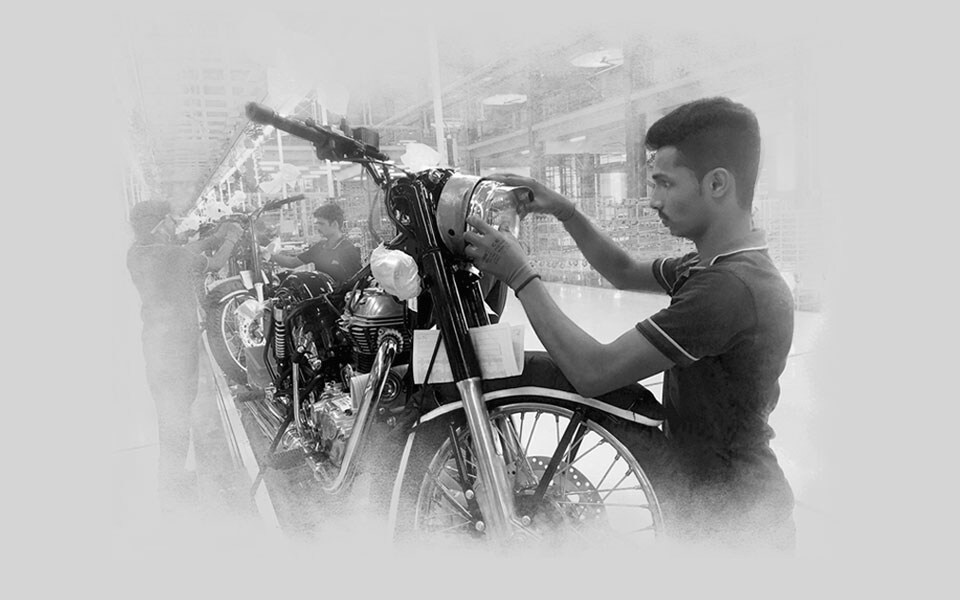

2017
Royal Enfield commences production from its third manufacturing facility at Vallam, near Chennai.
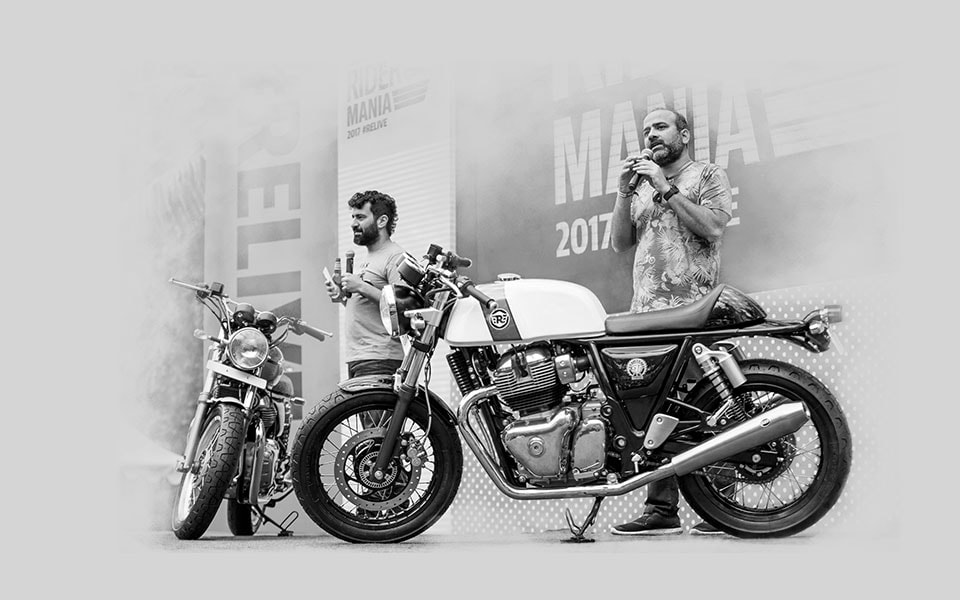

2017
Royal Enfield unveils ‘The Twins’ at the EICMA Motor Show, Milan and at Rider Mania, Goa, India
From Royal Enfield see link to Royal Enfield.com below

